Tolls on seven Bay Area bridges increased by $1 on New Year’s day fund $4.45 billion of transportation projects

The John A. Nejedly Bridge in Antioch. Source: BATA
Second of three voter-approved increases, this one to $7; funds held in escrow pending State Supreme Court decision

Bay Bridge Toll Plaza from MTC website. By Noah-Berger
By Bay Area Toll Authority
With the new year, the Bay Area Toll Authority (BATA) reminds drivers that tolls at the region’s seven state-owned toll bridges increased by $1 on Jan. 1, 2022. This is the second of the three $1 toll increases approved by the Legislature in 2017 through state Senate Bill 595 and by voters through Regional Measure 3 in June 2018. The first of these toll hikes went into effect on Jan. 1, 2019. The last of the Regional Measure 3 toll increases will go into effect on Jan. 1, 2025.
Regular tolls for two-axle cars and trucks (as well as for motorcycles) at the San Francisco-Oakland Bay, Antioch, Benicia-Martinez, Carquinez, Dumbarton, Richmond-San Rafael and San Mateo-Hayward bridges rose to $7 from the current $6 on Jan. 1, 2022.
Tolls for vehicles with three or more axles also rose by $1 on Jan. 1, 2022, at all seven of the state-owned toll bridges: to $17 for three axles, $22 for four-axles, $27 for five axles, $32 for six axles, and $37 for combinations with seven or more axles.
Senate Bill 595 and Regional Measure 3 continue the peak-period toll discount for motorcycles, carpools and qualifying clean-air vehicles crossing any of the state-owned toll bridges on weekdays from 5 a.m. to 10 a.m. and from 3 p.m. to 7 p.m. The discounted toll increased to $3.50 on Jan. 1, 2022, from the previous $3. To qualify for this discount, carpoolers, motorcyclists and drivers of qualifying clean-air vehicles must use FasTrak® to pay their tolls electronically and must use a designated carpool lane at each toll plaza.
Senate Bill 595 and Regional Measure 3 also established a 50-cent toll discount for two-axle vehicles crossing more than one of the state-owned toll bridges during weekday commute hours of 5 a.m. to 10 a.m. and 3 p.m. to 7 p.m. To be eligible for the toll discount, which is to be applied to the second toll crossing of the day, motorists must pay their tolls electronically with FasTrak®. Carpools, motorcycles and qualifying clean-air vehicles making a second peak-period toll crossing in a single day will qualify for an additional 25-cent discount off the already-discounted carpool toll.
Funding for Transportation Projects
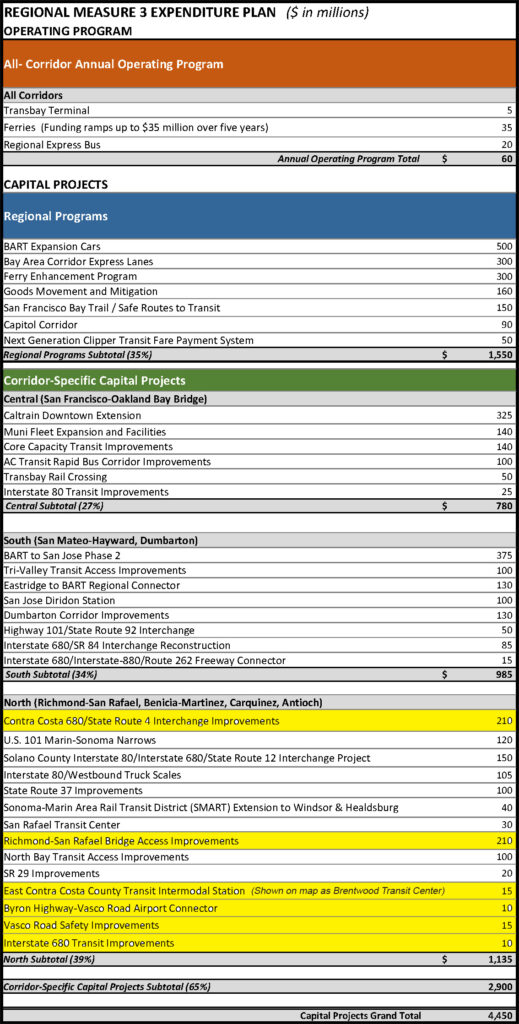
The funds collected from the additional toll will fund a $4.45 billion list of transportation improvement projects throughout the nine-county Bay Area, which includes $470 million in Contra Costa County.
Source: MTC
Source: MTC
New FasTrak® customers can obtain toll tags at hundreds of Walgreens and Costco stores around the Bay Area. A complete list of participating locations — as well as an online enrollment and registration feature — is available on the FasTrak® Web site at bayareafastrak.org. Customers also may enroll in the FasTrak® program by phone at 1-877-229-8655; by calling 511 and asking for “FasTrak” at the first prompt; or in person at the FasTrak® customer service center at 375 Beale Street in San Francisco. Phone service is available Monday-Thursday from 8 a.m. to 6 p.m. and on Fridays from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. The walk-in customer service center is open Monday-Friday from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. FasTrak® can be used in all lanes at all Bay Area toll plazas.
Because a legal challenge to Senate Bill 595 and Regional Measure 3 remains pending before the California Supreme Court, the January 1, 2022 toll increase, as collected, is placed into an escrow account managed by an independent trustee. Revenue from the 2019 toll increase also is being held in escrow. If BATA prevails in the litigation, the funds will be applied to BATA-approved programs.
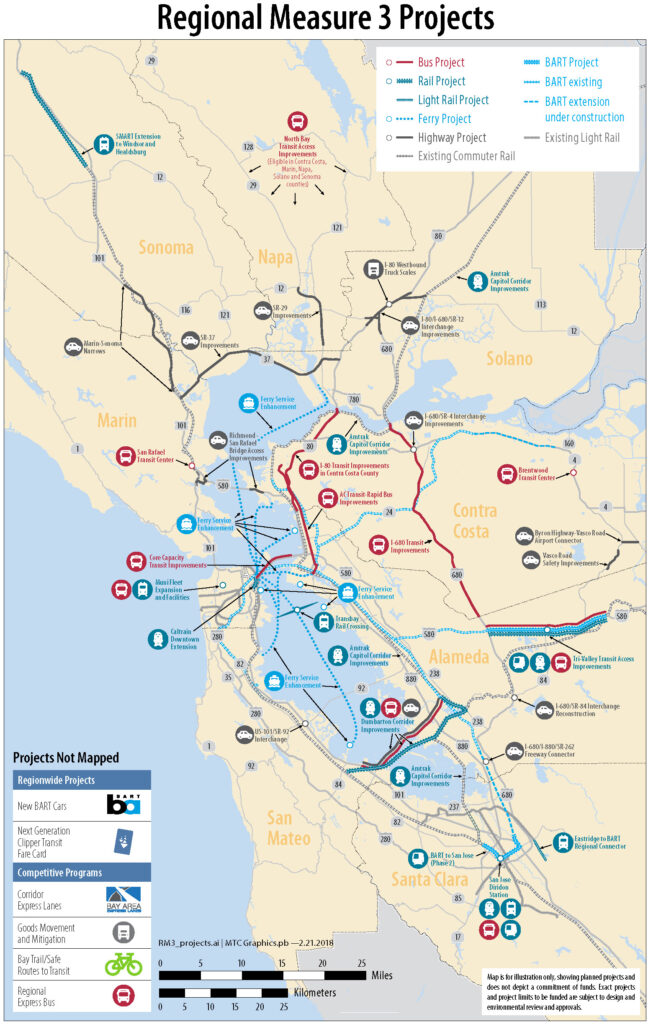
Major projects in the Regional Measure 3 expenditure plan include improvements to State Route 37 in the North Bay, freeway interchange improvements in Alameda, Contra Costa and Solano counties, the purchase of more new BART cars, extension of the BART system from Berryessa to downtown San Jose and Santa Clara, extension of the Caltrain corridor to the Salesforce Transit Center in downtown San Francisco, expansion of Muni’s transit vehicle fleet, expansion of San Francisco Bay Ferry service and more frequent transbay bus service, a direct freeway connector from northbound U.S. 101 in Marin County to the Richmond-San Rafael Bridge, upgrades to the Dumbarton Bridge corridor, and extension of the SMART rail system to Windsor and Healdsburg in Sonoma County.
BATA, which is directed by the same policy board as the Metropolitan Transportation Commission (MTC), administers toll revenues from the Bay Area’s seven state-owned toll bridges. Toll revenues from the Golden Gate Bridge are administered by the Golden Gate Bridge, Highway and Transportation District, which joined with BATA to operate a single regional FasTrak® customer service center in San Francisco. MTC is the transportation planning, financing and coordinating agency for the nine-county San Francisco Bay Area.
Allen Payton contributed to this report.
the attachments to this post:

Final_RM3_Expenditure_Plan Contra Costa projects